CD206 Antibodies (C-type 1 Lectin Receptor Antibodies)

- On This Page
- C-type 1 Lectin receptor antibodies
- CD206 antibody images
- CD206 antibodies
- References
C-type 1 Lectin receptor antibodies
CD206 is a pattern recognition receptor, also known as mannose receptor C type 1 (MRC1) that can recognize microbial carbohydrates and mediate phagocytosis. Members of the Mannose receptor family share a common extracellular domain structure, but with distinct ligand binding properties and cell type expression. This is a 162-175 kDa type -1 transmembrane protein and a member of the Group VI C-type lectins along with CD280 (ENDO180), CD205 (DEC205), and the phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R1).
CD206 is a complex molecule composed of a N-terminal cysteine-rich ricin b-type lectin domain (RICIN), a fibronectin type II domain (FN2), eight tandemly arranged C-type lectin like domains (CTLDs), a transmembrane domain (TM), and a cytoplasmic domain. The terminal cysteine-rich domain of CD206 binds sulphated sugars, while CTLDs 4 to 8 recognize polysaccharides terminated in mannose, fucose, or N-acetylglucosamine. These sugars are all found on microorganisms and on some endogenous glycoproteins.
This marker is found on cells that constitute barriers (such as keranocytes, lymphatic and hepatic epithelium, kidney mesangial cells, tracheal smooth muscle and retinal pigment epithelium) and antigen presenting cells (including macrophages, human monocyte derived dendritic cells, and some subpopulations of mouse dendritic cells). For detailed information on macrophages see our macrophage polarization mini-review.
Functionally CD206 is active in antigen processing, endocytosis and phagocytosis, playing an important role in the innate immune response.
Two anti human clones are available; clone 7-450 was designed specifically for use with frozen immunohistochemical sections, and clone 15-2, is more versatile excelling in applications such as flow cytometry, western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
CD206 antibody images

Fig 1. MRC1 (CD206). Uniprot:P22897.

Fig 2. Crystal structure of the cysteine-rich domain of mannose receptor represented in a line ribbon colored by residue. Protein Data Bank (PDB: 1DQO) image generated using WebLab Viewer.
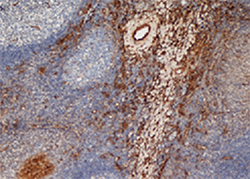
Fig 3. Staining of frozen human tonsil stained with mouse anti human CD206 antibody (MCA2519).
CD206 Antibodies
| Description | Target | Format | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|
Searching for your antibody of choice is made easy by the use of the sophisticated filter table, which allows you to select for specific antibody parameters. If you are unable to find your desired antibody simply contact us as we are adding new product all the time and we will be happy to help advise you.
References
-
Emara, M. et al. (2011) Recognition of the major cat allergen Fel d 1 through the cysteine-rich domain of the mannose receptor determines its allergenicity.
J Biol Chem. 286:13033-40. -
Ueno, N. et al. (2009) Differences in human macrophage receptor usage, lysosomal fusion kinetics and survival between logarithmic and metacyclic Leishmania infantum chagasi promastigotes.
Cell Microbiol. 11: 1827-41. -
Yamamoto, H. et al. (2011) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine and lysosulfatide have inverse regulatory functions in monocytic cell differentiation into macrophages.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 506: 83-91.





