CD209 (DC-SIGN): An Immunomodulating Pattern Recognition Receptor

- On This Page
- Overview
- Human and mouse CD209 antibodies
- CD209 antibodies
- Additional reading
Overview
CD209, originally called DC-SIGN (dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin), is a 45 kDa type-2 transmembrane protein that belongs to the group II C-type lectins. Expressed on myeloid monocyte derived dendritic cells, subpopulations of macrophages, and some endothelial cells, it functions primarily in dendritic cell migration and interactions with naïve T lymphocytes.
Structurally, the C-terminus of CD209 is made up of a C-type lectin-like domain (CTLD) joined to a multi-section stalk region. This is followed by a transmembrane portion and a cytoplasmic tail. The stalk region aids in tetramerization, while the cytoplasmic tail contains internalization motifs in humans.
CD209 binds to an interesting range of molecules in its role as an immunomodulator. For example, it participates in T-cell activation by binding CD50 (ICAM-3) and it facilitates transendothelial migration via binding to CD102 (ICAM-2). It also binds the HIV gp120 protein and other mycobacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens through recognition of mannose structures on their surfaces. Even though internalization motifs are present on primate CD209, and there are suggestions that it is a phagocytic receptor, the immunomodulatory role of DC-SIGN is mainly related to dendritic cells.
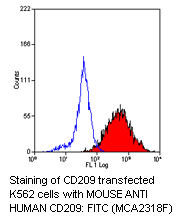
Human and Mouse CD209 Antibodies
Bio-Rad manufactures antibodies specific for human and mouse CD209.
Anti-human CD209 antibody (MCA2318, clone MR-1) antibody can be ordered in a purified format, or in a low endotoxin version for functional studies; both forms are guaranteed for immunofluorescence. Conjugates are available to Alexa Fluor® 488, Alexa Fluor® 647, Biotin, FITC, and RPE. All formats are suitable for flow cytometry, and can be obtained in smaller vial sizes for testing.
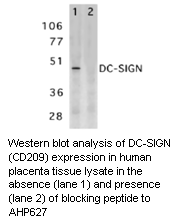
We also offer AHP627, a polyclonal antibody specific for human CD209, which is suitable for Western Blotting.
CD209 Antibodies
| Description | Target | Format | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|
Additional reading:
-
Zhou T.C., et al. (2006) DC-SIGN and immunoregulation.
Cell Mol. Immunol. 3(4):279-83 -
den Dunnen J., et al. (2009) Innate signaling by the C-type lectin DC-SIGN dictates immune responses
Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 58(7):1149-57





