Autophagy Products and Resources

- On This Page
- Products
- Resources
Best practices, such as careful sample preparation, are vital for accurate measurement of autophagy. On this page, we provide hints and tips to achieve great results using Autophagy Probe Red.
Products
Easy-to-Use Kits and Antibodies
The progression down the orderly process of autophagy can be an early indication of poor cell health due to starvation or growth factor suppression, ER stress, infection, or immune signals.
We offer a range of antibodies and kits to detect and measure markers of autophagy. These include reagents to detect the lysosome, the autophagosome, and the most studied macroautophagy pathway.
For more information on autophagy and a more comprehensive list of autophagy antibodies, including the ATG proteins responsible for regulation of the autophagy machinery, visit our dedicated autophagy page.
Autophagy Kits
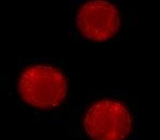
Fig. 1. Staining of staurosporine-induced THP-1 cells using the Magic Red Cathepsin B Kit.
Autophagy Probe Red is a cell-permeant aliphatic molecule that fluoresces brightly when inserted into the lipid membranes of autophagosomes and autolysosomes. Fusion of the autophagosome with a lysosome to form an autolysosome is crucial to allow enzymes such as cathepsins to hydrolyze cargo for recycling back to the cytoplasm.
A quick and easy method to determine cathepsin B, K, and L levels in lysosomes of both adherent and suspension cells is to use our Cathepsin Green and Magic Red Kits™
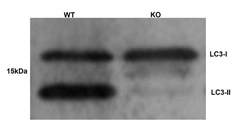
Fig. 2. Western blotting analysis of LC3 expression on Atg5 knockout and wild type cells using Rabbit anti-Human MAP1LC3A/B (AHP2167). Image courtesy of Dr. R. Kopito, Stanford University.
Autophagy Antibodies
We have antibodies to detect common markers of autophagy. These include Beclin-1, which is one of over 30 autophagy proteins involved in the regulation of the pre-autophagosomal structure. Another reliable method of monitoring autophagy is to use the mammalian homologue of ATG8, MAPILC3A/B.
These ubiquitin-like proteins are found in autophagosomes. Autophagy can be measured by changes in cellular localization and detection of two bands by western blot due to the presence of cytosolic LC-I and PE bound LC-II.
The macroautophagy pathway can be studied using antibodies against lysosome-associated membrane proteins LAMP 1 & 2 (CD107a and b).
Autophagy is only one aspect of cell health. We have antibodies, reagents, and kits to detect viability, proliferation, and apoptosis to have confidence in your cell health.
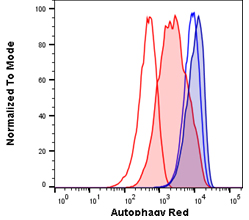
Fig. 3. Autophagy induction in Jurkats measured with different amounts of Autophagy Probe Red (APO010). Jurkat cells were either untreated for basal conditions (open histograms) or serum starved by incubation in Hanks balanced salt solution (HBSS) and in the presence of bafiloymin A1 (solid histograms) to induce high levels of autophagy. Cell staining with a 1:50 dilution of Autophagy Probe Red for 30 min (red histograms) or a 1:20 dilution for 60 min (blue histograms). Cells were washed and analyzed on the ZE5 Cell Analyzer.
Resources
Best Practice for Detecting Autophagy by Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique that allows you to identify and analyze large numbers of cells in a mixed population.
This enables the detection and quantification of autophagy in specific cells without preenrichment or sorting for your cell type of interest, which is time consuming and can stress cells leading to false positives.
Performing flow cytometry over a time course can reveal how the process develops and can be used as an early screening method, allowing high sample throughput. Careful experimental set-up and interpretation of data is discussed here to make the most of your results.

Autophagy Overview
Mini-Review
Autophagy in the Immune System and in Malignancy
Autophagy has a complex dual role in cell survival and cell death and has been rigorously studied in relation to the immune system and in cancer, particularly in the role that the immune system plays in the removal of malignant cells. Autophagy can promote or inhibit tumor development depending on the cell type and tumor stage.
How autophagy regulates the immune system to attack malignant cells is therefore of interest (Jiang et al. 2019). Many anti-cancer therapies attempt to modulate autophagy, for example using autophagy related gene (ATG) inducers/inhibitors or preventing autophagosome-lysosome fusion, with the aim to enhance the immune response and anti-tumor effects of immunotherapies (Cuomo et al. 2019).
There have been many recent studies on autophagy, demonstrating the importance of this process in modulating immune cells of both the innate and adaptive immune systems.
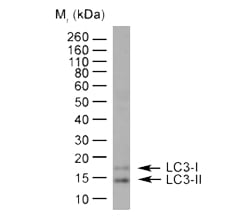
Fig. 4. Detection of LC31/11 by western blotting. HeLa lysate probed with Rabbit anti-Human LC3A/B (N-terminal) (AHP2167) followed by horseradish peroxidase conjugated Sheep anti-Rabbit IgG Antibody. As can be seen in the blot, LC3-I and LC3-II can be clearly distinguished from each other.
Effective Detection of Autophagy
Autophagy is a vital cellular process involved in keeping the immune system working properly and has been linked to a number of diseases, including malignancies. Multiple components of the autophagy pathway can be detected, allowing researchers to efficiently study the process. These include:
- Signaling molecules involved in autophagy induction, such as mTOR and AMPK
- LC3-I and LC3-II. LC3-I is a protein found in the cytosol which becomes lipidated to form LC3-II and is inserted into the membrane of autophagosomes
- Other autophagy-related proteins, like ATG5-12 complex and WIPI1
- Lysosome mass
- Lysosomal markers, such as LAMP1 and LAMP2
These markers tell us about specific components of the autophagy pathway. An alternative method is to measure autophagy activity, also known as autophagy flux. This is a measurement of the whole autophagic process from induction, autophagosome formation, fusion with lysosomes, and breakdown of the autophagosome contents.
There are different techniques and assays that can be used to investigate autophagy, click the button to find out more including the pros and cons of each approach, which are discussed in more detail on our autophagy detection page.




